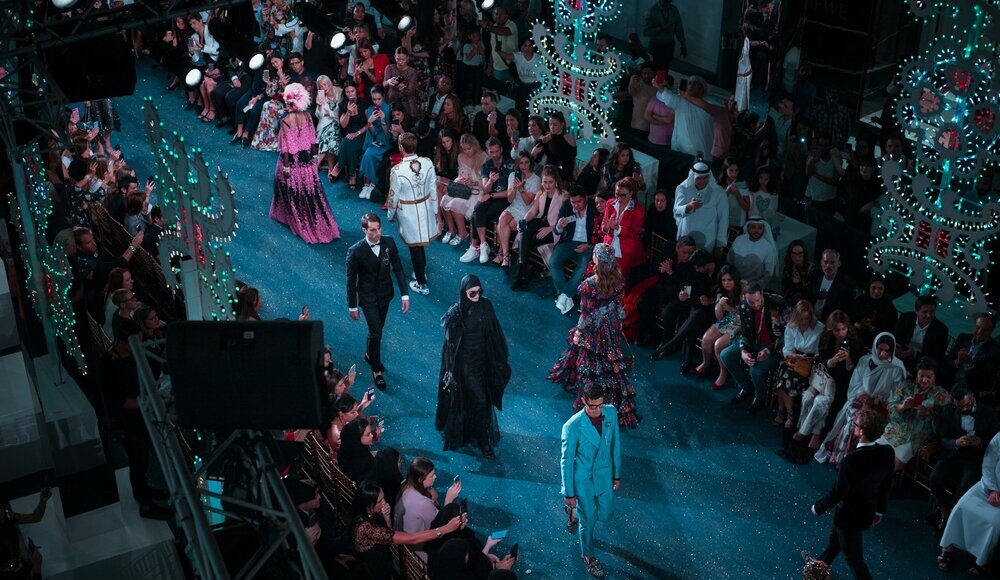
Fashion Weeks in the “Big Four” fashion capitals – New York, London, Milan, and Paris – have a significant economic impact on local industries during the event weeks.
Below, we break down the most recent available figures (as of 2023–2025) for key sectors like hotels, restaurants, retail, transportation, and related areas in each city.
Overall Economic Impact:
New York Fashion Week takes place twice a year (in February and September). It generates roughly $887 million in total economic impact annually for NYC, including about $547 million in direct visitor spending during those weeks. More than 230,000 people attend the fashion shows in person each year, and including trade shows and showrooms, over 500,000 visit during the NYFW season. This makes NYFW’s economic impact comparable to, or even greater than, events like the U.S. Open or the NYC Marathon.
Hotels & Accommodation:
The influx of fashion designers, models, buyers, media, and tourists fills New York’s hotels to near capacity. During Fashion Week, hotel occupancy rates and prices surge dramatically. For example, in the lead-up to NYFW, average NYC hotel rates jump by ~52% (from about $347 to $526 per night. Luxury hotels often charge premium prices and still achieve occupancy in the mid-80s to 90% range, reflecting Fashion Week-driven demand (for context, once the concurrent UN General Assembly arrives, rates spike even higher, but Fashion Week alone creates a hefty bump). This scarcity effect trickles down to mid-range and budget hotels as well, which see unusually high rates due to overflow demand.
Restaurants & Nightlife:
New York’s dining industry sees a notable uptick during Fashion Week. Thousands of visitors and industry insiders dining out translate to fully booked restaurants, longer wait times, and increased spending. High-end restaurants report a surge in reservations, and even casual eateries and food trucks share in the boom. In Fashion Week season, “reservations soar, wait times extend,” and the city’s culinary scene – from Michelin-starred venues to street vendors – enjoys a feast of increased patronage. Bars, clubs, and event venues also benefit from Fashion Week parties and events, further boosting hospitality demand.
Retail & Shopping:
The city’s retail sector experiences a Fashion Week bounce as well. Many attendees use the opportunity to shop the latest trends, and boutiques and flagship stores see higher foot traffic and sales volumes during Fashion Week. Luxury retail corridors (like Fifth Avenue and SoHo) report sales “climbing” during NYFW thanks to fashion-conscious tourists and influencers purchasing items and showcasing them online. It’s not uncommon to spot a maltipoo perched in a handbag as influencers stroll between stores, capturing street style shots that double as shopping inspiration. The presence of social media influencers and online retailers in town further amplifies retail activity, driving both in-store and online sales for fashion brands.
Transportation & Other Services:
With so many visitors in the city, transportation services see increased usage. Taxis, ride-hailing services, and public transit handle extra demand as people shuttle between shows and events. Event production and media services also ramp up, with temporary jobs for drivers, couriers, stage crews, photographers, etc., multiplying to support the shows. In fact, NYFW brings a broad employment boost across creative and logistical fields – from makeup artists and stylists to livestream technicians – highlighting how Fashion Week touches many corners of the local economy.
(New York’s fashion industry at large is a massive year-round employer – over 180,000 jobs in the city, paying $11 billion in wages, and the Fashion Week events act as biannual catalysts for tourism and spending across these sectors.)
London (London Fashion Week – LFW)
Overall Economic Impact:
London Fashion Week, held twice a year, is slightly smaller in scale than NYFW but still delivers an outsized economic boost. Recent analyses estimate that LFW contributes around £269 million to the UK economy per year. (This is equivalent to roughly $370–$375 million USD.) The British Fashion Council noted that London’s fashion industry overall generates £32 billion annually for the UK, with LFW as a key flagship event. Each LFW attracts a substantial professional crowd, despite London’s shows being fewer than those in Paris or New York: over 5,000 industry professionals from more than 70 countries attend each season.
Tourism, Hotels & Hospitality:
International visitors flock to London Fashion Week, and they fill the city’s hotels and restaurants throughout the week. In parliamentary discussion, officials highlighted that LFW’s overseas guests “stay in our hotels, eat in our restaurants, use our transport system” – underscoring its importance for London’s hospitality sector. Upscale hotels near the event venues tend to sell out early and often raise rates during LFW due to increased demand. The city is large enough to absorb the influx, but central London accommodations do see notably higher occupancy and pricing during Fashion Week. Restaurants, cafés, and pubs in fashion-centric areas (such as Soho, Covent Garden, and Shoreditch) report crowds of fashion insiders during LFW, often hosting special events and late-night parties that boost their revenue.
Retail & Shopping:
London’s retail sector – from luxury department stores to independent boutiques – enjoys heightened activity during Fashion Week. The event showcases British designers and attracts global buyers, often resulting in orders and sales. In fact, London Fashion Week’s direct economic impact (≈£269M) includes robust spending in retail. Central shopping districts (Oxford Street, Bond Street) see increased foot traffic from Fashion Week attendees and tourists. Additionally, British brands often align product launches or pop-ups with LFW to capture consumer enthusiasm. It’s also common to see trend-driven offerings, from capsule collections to permanent jewelry activations, timed to coincide with Fashion Week buzz. The UK fashion industry’s clout (over 500,000 jobs and £60+ billion market size) is on display during LFW, and retail sales get a seasonal lift from the event.
Transportation & Media:
London’s public transport and transit options handle extra riders as attendees shuttle to runway venues across the city. The London Underground and black cabs see upticks in ridership during show times, particularly on routes to central London event hubs. Media production is also in high gear: LFW draws extensive press coverage and content creation. While numeric values are hard to pin down, it’s clear that global fashion media focus on London this week, generating marketing value. (For example, London Fashion Week’s media impact has been reported in the hundreds of millions of dollars in exposure.) Local production companies, staging crews, and freelancers also get busy – the event provides jobs for photographers, PR agencies, event staff, and more.
Milan (Milan Fashion Week)
Overall Economic Impact:
Milan hosts multiple Fashion Weeks each year (women’s in February and September, men’s in January and June), making it a fashion powerhouse. The women’s Fashion Week in Milan each season generates a significant boost: for instance, the September 2025 women’s Fashion Week was projected to inject about €239 million (euros) into Milan’s economy. This was an increase of 12% over the previous year’s edition, indicating growth. For context, the February 2025 Fashion Week had an economic impact of around €185 million, so the women’s wear shows alone approach €420 million annually. Including the menswear weeks and other related events, Milan’s total Fashion Week-driven economic impact likely exceeds €500 million in direct spending per year. (Older industry estimates put it around £160 million, but recent figures are clearly higher.)
Visitor Numbers & Tourism:
During a typical Milan Fashion Week, over 149,000 visitors come to the city specifically for the shows and events. About 46% of these are international visitors flying in from around the world – underscoring Milan’s global draw. The remaining attendees travel from within Italy to partake in the fashion festivities. This surge of tourists has a measurable effect on local businesses. Each visitor spends an average of about €1,600 during their stay in Milan. Milanese hotels, especially luxury and boutique hotels in the city center, see very high occupancy. It’s reported that hospitality and dining account for roughly 39% of the total spending during Fashion Week, equivalent to over €93 million in a single week. In other words, hotels and restaurants enjoy a windfall from fashion visitors.
Hotels & Restaurants:
Hotels in Milan sell out during Fashion Week, with many fashion houses, buyers, and media booking blocks of rooms. Room rates often rise due to supply compression (as in NYC). The Confcommercio research data for Milan Fashion Week shows €93+ million spent on hotels and restaurants during the week. Fine dining restaurants and bars in districts like Brera, Navigli, and the fashion district (Quadrilatero) are filled with designers and models entertaining clients. Local restaurateurs have noted Fashion Week as a peak period for business, second only perhaps to major trade fairs. The culinary sector (from five-star dining to casual cafes) pulls in nearly 40% of Fashion Week visitor expenditures.
Retail & Shopping:
It’s no surprise that shopping is the top expenditure during Milan Fashion Week, as the city is known for fashion boutiques and luxury stores. About 46% of Fashion Week visitors’ spending goes toward shopping, amounting to roughly €110 millionthat week. Milan’s Via Montenapoleone and Galleria Vittorio Emanuele II attract throngs of buyers and fashion enthusiasts who purchase luxury goods. Many fashion show attendees use their downtime to visit the flagship stores of Italian brands. The immediate boost in retail sales during Fashion Week is significant – boutiques report higher sales figures and often extend hours to accommodate the influx of shoppers. The events themselves (runway shows and showroom appointments) also lead to large orders placed by buyers for the next season, driving future production and wholesale revenue (though those transactions’ value isn’t counted in the local spending figure).
Transportation & Other Services:
Transportation services in Milan surge as well – roughly 15% of Fashion Week spending (≈€35.8 million) is allocated to transportation. This includes everything from taxis and chauffeur services that shuttle guests to venues to flights and trains that bring in visitors. Milan’s airports see spikes in private jet and commercial arrivals for Fashion Week, and local transit (metro, trams) is bustling with increased ridership. Other industries benefit too: event production companies, staging and lighting technicians, security personnel, caterers, and freelance translators (for international press) all share in the Fashion Week pie. The trade show and exhibition sector in Milan often aligns with Fashion Week (e.g., fabric and textile fairs held around the same time), further multiplying economic activity. Milan’s Chamber of Commerce has highlighted that these fashion events are “a driving force not only for creativity, but also for the economy”, creating real opportunities for hoteliers, restaurateurs, retailers, transport providers, and creative professionals alike.
Paris (Paris Fashion Week – PFW)
Overall Economic Impact:
Paris hosts multiple fashion weeks – including the major women’s Ready-to-Wear Fashion Weeks (spring and fall), Haute Couture Week, and Men’s Fashion Week – making Paris Fashion Week the longest and arguably most significant. Paris Fashion Week spans about 38 days of shows per year in total (across those events). According to the French Fashion Federation, the shows and events of Paris Fashion Week generate over €400 million in direct economic activity each year for Paris. And when you include the trade fairs linked to Fashion Week (attended by tens of thousands of fashion professionals), the total expenditure rises to over €1.2 billion per year in Paris. This massive figure underscores Paris’s position as the world’s fashion capital. In fact, one analysis in 2023 found that Paris Fashion Week delivered an estimated $1.36 billion USD in economic benefit, higher than New York’s, making it the top fashion week in monetary terms (plus500.com).
Hotels & Accommodation:
During Paris Fashion Week, hotels reach near-full capacity with designers, celebrities, journalists, and buyers flooding the city. It’s common for 5-star and boutique hotels to be fully booked months in advance of PFW. Paris often sees hotel occupancy in the 90%+ range during big show days. For example, during one recent menswear week, hotel occupancy reached 93.6% on the peak night, with average daily rates in Paris hotels soaring above €520. Luxury hotels and palace hotels host numerous brand events and see their suites occupied by VIP clients. Even mid-range hotels benefit from overflow demand. The influx of Fashion Week guests “sets the entire Paris economy in motion: hotels fill up, restaurants are packed”, as one account describes. Paris’s hospitality industry eagerly anticipates these fashion seasons, as they bring a spike in revenue comparable only to events like the Olympics or World Cup in scale.
Restaurants & Entertainment:
Paris’s restaurants and cafés thrive during Fashion Week. The city’s fine dining establishments report fully booked tables with fashion industry reservations for lunches and dinners in between shows. High-profile venues (often the sites of after-parties) are packed with designers and models. Even casual bistros and pastry shops in the central arrondissements notice increased patronage. Local brasseries, bars, and nightclubs are open later and host special Fashion Week events, drawing big-spending clientele. This surge is reflected in the spending data: a large portion of visitor expenditure in Paris goes to food and entertainment. Museums and cultural attractions also see record crowds from the mix of tourists in town for Fashion Week – many visitors mix fashion events with sightseeing. In short, Paris’s culinary and nightlife scene experiences one of its busiest periods of the year during Fashion Week, second only to perhaps peak summer tourism.
Retail & Luxury Shopping:
As the home of haute couture and luxury maisons, Paris sees a shopping bonanza during Fashion Week. International buyers and wealthy clients take the opportunity to visit flagship stores of Chanel, Dior, Louis Vuitton, Hermès, and others, often scheduling private shopping appointments. The Champs-Élysées, Avenue Montaigne, and Rue Saint-Honoré buzz with fashion week attendees purchasing the latest collections. According to the Paris tourism office, tax-free shopping by foreign visitors spikes during Fashion Week, contributing significantly to Paris’s retail revenues. The Google Arts & Culture study notes that the fairs and showrooms around Paris Fashion Week bring tens of thousands of professionals who collectively spend hundreds of millions on fashion orders. While those wholesale orders aren’t immediate retail sales, they underscore how Paris Fashion Week drives global fashion commerce. On the consumer side, fashion enthusiasts in town spend freely on clothing, accessories, and cosmetics, giving Paris’s retail sector a healthy boost each season.
Transportation & Media Production:
Paris’s transport infrastructure is heavily utilized during Fashion Week. Air travel into Paris surges – flights (and even private jets) bring in fashion VIPs from around the world. In total, around 100,000 industry insiders travel to Paris for Fashion Week, making it a major driver of airline and train bookings. Within the city, taxis and ride-share vehicles run nonstop, ferrying people to back-to-back shows. The Paris Metro sees increased ridership, especially on lines serving Grand Palais, the Louvre, and other venue areas. Additionally, media and production crews are ubiquitous: Paris Fashion Week is covered by press from dozens of countries. In terms of media production, the advertising/media exposure value of Paris Fashion Week is enormous – one recent Paris Fashion Week generated $1.1 billion in media impact value within 48 hours of its conclusion, nearly matching the Cannes Film Festival’s media footprint. This indicates how much content (photography, video, live streams, social media) is produced during the event. Local production companies, event staff, PR agencies, and technical crews all see high demand. Paris Fashion Week is not only about runways but also about countless photoshoots, product launches, and networking events happening across the city, all of which require logistical support and boost economic activity.
##